In today’s digital era, the real estate industry has seen significant shifts, particularly with the rise of online platforms such as Multiple Listing Service (MLS) portals. These portals are central to modern real estate transactions, connecting buyers, sellers, and agents in a seamless digital environment. However, with the increasing reliance on technology comes the escalating threat of cyberattacks. MLS portals, which store vast amounts of sensitive data including personal information, financial details, and property listings, are prime targets for hackers.
This article delves into effective cybersecurity strategies for MLS portals, exploring potential threats and offering comprehensive solutions to secure these platforms from cyber risks. From understanding the key vulnerabilities to implementing layered security protocols, this guide provides real estate businesses with the necessary tools to protect their online operations.
The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity in MLS Portals
MLS portals have transformed the real estate sector, enabling users to search for properties, view listings, interact with agents, and even complete transactions—all from the comfort of their homes. However, these platforms have also become attractive targets for cybercriminals. In recent years, the real estate industry has witnessed a sharp increase in cybercrime incidents, including data breaches, identity theft, and ransomware attacks. The sensitive nature of the data stored in MLS portals, including contact information, transaction history, and financial details, makes them highly valuable to hackers.
While cybersecurity is crucial for any online business, MLS portals face unique challenges due to the combination of various stakeholders involved in real estate transactions. These include buyers, sellers, brokers, and third-party services such as mortgage lenders. The need for comprehensive security strategies to protect the integrity of these interactions has never been more urgent.
Common Cybersecurity Threats for MLS Portals
To devise effective cybersecurity strategies, it is essential to understand the specific threats faced by MLS portals. Below are some of the most common cyber risks associated with these platforms:
Data Breaches
Data breaches remain one of the most prevalent cybersecurity threats. These occur when unauthorized individuals gain access to confidential data, such as client personal information or payment details. In the context of MLS portals, a data breach can lead to significant financial losses, legal repercussions, and a damaged reputation.
Phishing Attacks
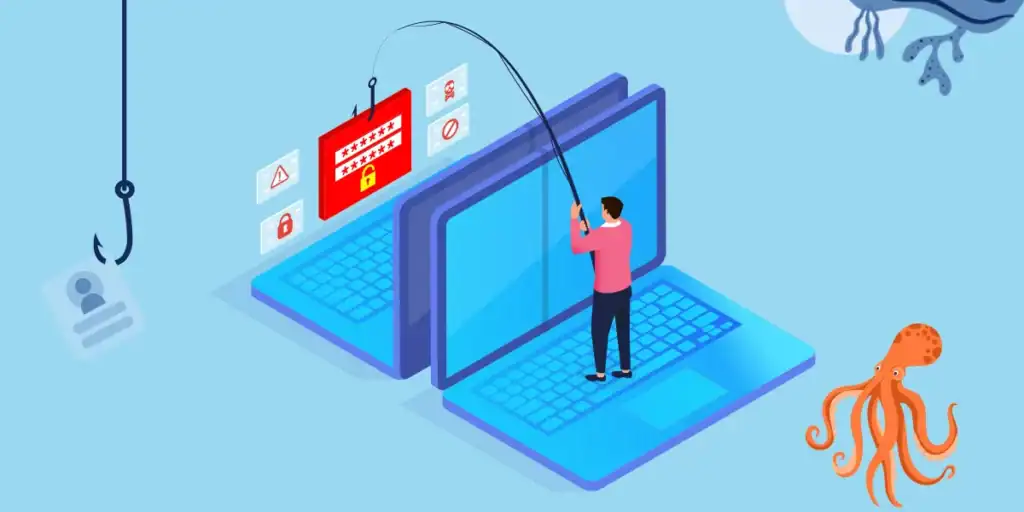

Phishing is a social engineering attack in which cybercriminals impersonate legitimate entities, such as real estate agents or lenders, to trick users into revealing sensitive information. In MLS portals, phishing attacks often take the form of emails or messages that appear to be from trusted parties, asking users to click on malicious links or download infected attachments.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware involves the encryption of critical files by cybercriminals, who demand a ransom in exchange for the decryption key. For MLS portals, a ransomware attack could cripple operations, leading to significant downtime and loss of business continuity. It could also jeopardize client data, further exacerbating the impact.
SQL Injection
SQL injection is a type of attack where malicious code is inserted into SQL queries via input fields, enabling attackers to access, modify, or delete data from the database. Given that MLS portals store vast amounts of structured data, they are susceptible to SQL injection attacks if not properly secured.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
MitM attacks occur when an attacker intercepts communication between two parties, such as between a user and the MLS portal. These attacks are especially concerning when users transmit sensitive data, such as credit card details or personal information, over insecure networks. Cybercriminals can steal this data or modify it without either party knowing.
Essential Cybersecurity Strategies for MLS Portals
Now that we understand the types of cyber threats facing MLS portals, let’s explore the essential cybersecurity strategies that can be implemented to mitigate these risks.
1. Data Encryption
Data encryption is one of the most critical cybersecurity measures for MLS portals. This process converts data into an unreadable format, which can only be decrypted by authorized parties with the correct key. By encrypting sensitive information both at rest and in transit, MLS portals ensure that even if hackers gain access to the data, they will be unable to read or use it.
- SSL/TLS Encryption: One of the most common encryption methods for web applications is the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS). These protocols encrypt data transmitted between the client and the server, ensuring that any sensitive data, such as login credentials and payment information, remains secure during transactions.
- Database Encryption: For data stored within the MLS portal’s database, it is important to employ encryption algorithms to protect user data from unauthorized access. This is particularly vital for client information, such as names, addresses, phone numbers, and transaction history.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds a layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before gaining access to their accounts. For MLS portals, this typically involves something the user knows (password), something the user has (a mobile device or token), or something the user is (biometric authentication such as fingerprints or facial recognition).
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: MFA is highly effective in preventing unauthorized access, even if a hacker has managed to obtain a user’s password. By requiring a second form of authentication, MLS portals make it much harder for attackers to break into user accounts.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Another best practice is implementing RBAC within the MLS portal. With RBAC, users are assigned specific roles, each with distinct permissions to access certain data or features. This reduces the risk of insiders or external attackers gaining unauthorized access to sensitive information.
3. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Continuous monitoring and testing of security protocols are crucial to identify vulnerabilities before cybercriminals can exploit them. Regular security audits and penetration testing help evaluate the strength of the MLS portal’s defenses.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct regular vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses in the portal’s software or infrastructure. These scans can help detect outdated software, missing security patches, or misconfigured settings that could be exploited by attackers.
- Penetration Testing: Penetration testing, also known as ethical hacking, involves simulating cyberattacks to identify vulnerabilities in the system. By proactively testing the system’s defenses, real estate firms can address any security gaps before they are exploited.
4. Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
In the event of a cyberattack, it is essential to have a solid backup and disaster recovery plan in place. This ensures that MLS portals can quickly recover from attacks such as ransomware or data breaches without significant disruptions to operations.
- Data Backups: Implement regular data backups to external servers or cloud storage. These backups should be encrypted and stored in multiple locations to ensure data can be restored quickly in case of a breach or system failure.
- Disaster Recovery Testing: Conduct periodic disaster recovery drills to ensure that your team is prepared to respond effectively in the event of an attack. These drills should simulate various cyberattack scenarios, including data loss, ransomware, and system outages.
5. User Education and Awareness
One of the most effective ways to prevent cyberattacks is by educating users on best practices for online security. For MLS portals, this includes educating both employees and clients about common cyber threats and how to avoid falling victim to them.
- Phishing Awareness Training: Regularly conduct phishing awareness training for employees and users of the MLS portal. This training should cover how to recognize phishing attempts, how to verify legitimate communications, and how to report suspicious activities.
- Password Management: Encourage users to create strong, unique passwords for their MLS portal accounts. Password managers can help users securely store and manage their passwords, reducing the risk of password reuse and weak passwords.
6. Secure APIs and Third-Party Integrations
Many MLS portals integrate with third-party services, such as mortgage lenders, payment processors, and marketing platforms. Each third-party integration introduces potential security risks, particularly if these services have weak security measures in place.
- API Security: Secure all APIs used by the MLS portal by implementing authentication protocols such as OAuth. This ensures that only authorized parties can access or send data to the API.
- Third-Party Vendor Assessments: Perform thorough security assessments on any third-party vendors or partners that integrate with the MLS portal. Ensure that they comply with industry-standard security practices, such as encryption and secure data storage.
7. Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Many countries have strict data privacy laws that govern how personal information is collected, stored, and processed. MLS portals must ensure compliance with these regulations to avoid legal penalties and build trust with users.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Compliance with GDPR is essential for MLS portals operating in or serving users in the European Union. GDPR mandates strict rules on data collection, storage, and consent, with significant penalties for non-compliance.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): In the United States, MLS portals must comply with the CCPA if they handle the personal data of California residents. The CCPA gives users greater control over their personal information and mandates transparency in data collection practices.
Conclusion
As MLS portals evolve as vital tools in the real estate industry, their cybersecurity cannot be overlooked. Implementing robust cybersecurity strategies is essential to protect sensitive data, ensure business continuity, and maintain user trust. By adopting a multi-layered security approach, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and user education, MLS portals can safeguard themselves against the growing threat of cybercrime.
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation to new threats. Real estate businesses must remain proactive, continuously improving their security measures to keep pace with the evolving landscape of cyber risks. With the right strategies in place, MLS portals can thrive in a secure digital ecosystem, providing valuable services to their users while minimizing the potential for cyber threats.